그룹웨어 시스템에서 사용자에게 도착한 메시지,전자결재 내역을 실시간으로 알림을 보내줄 기능을 구현하기위해
웹소켓, Pooling, Sse등 다양한 방법을 찾아보다가, Server-sent-event 방식이 가장 적합하다고 생각하여
Sse를 통해 실시간 알림 기능을 구현해보려고 한다.
관련자료를 찾아보는데 스프링 부트에서 구현한 예제밖에없어서 나는 스프링 레거시에서 진행하고있기에
아예 Sse에 대해 기초부터 공부한뒤 직접 적용시켜볼 예정이다.
우선 맨 처음 클라이언트에서 서버로 연결을 요청하는 것부터 해보았다.
클라이언트 -> 서버로 구독 요청하기
클라이언트 :

클라이언트는 맨 처음 서버에 요청을 보낼때 구독 요청을 하기위해 EventSource 객체를 생성하여
"/connect" 경로로 요청을 보낸다. 해당 경로로 addEventListener()를 통해 이후 서버에서 보내는 데이터들을
eventSource로 받게된다.
즉, 서버에서 보낸 eventsource의 name이 'firstconnect'인 데이터의 data값을 콘솔에 출력한다는 뜻이다.

클라이언트에서 보내온 요청을 받는 "/connect" 매핑된 컨트롤러이다. Sse를 사용하기위하여 스프링 프레임워크에서 지원하는 SseEmitter를 사용한다.
해당 컨트롤러는 클라이언트가 보낸 처음 보낸 요청을 받기위한 메소드로, SseEmitter 객체를 생성하여
맨 처음 더미데이터( name : firstconnect, data : connected!! )를 보낸다.
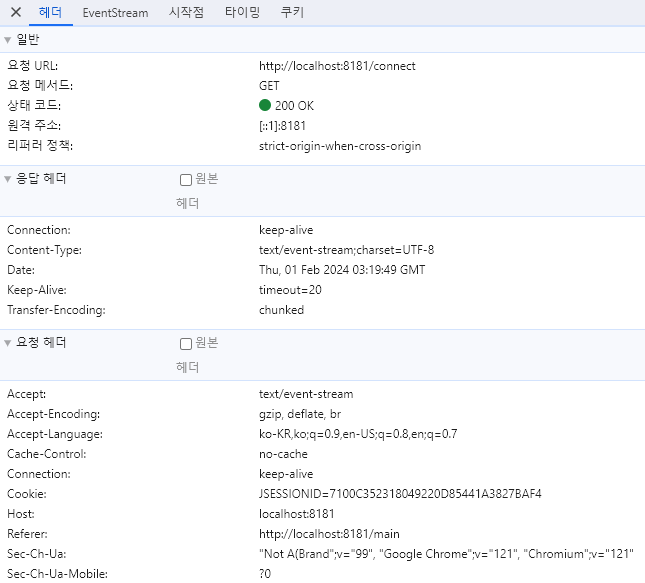
정상적으로 연결되었다.
이제, 클라이언트와 서버가 연결이 되었으니 서버에서 특정 이벤트가 발생하면 클라이언트에게 언제든지 emitter객체를 통해 응답을 보내줄수 있다.
나의 경우, 그룹웨어 시스템의 메신저 기능에서 누군가 메시지를 작성하면 받는사람에게 알림이 전송하도록 구현할것이다.
위의 경우 단 1번의 연결만을 위해 emitter객체를 저장하거나, Service 기능을 구현하지않았으므로 조금더 구체화해서
Emitter 클래스를 만들어야한다.
전체적인 로직 순서는
1. 클라이언트와 서버간 Sse 구독 요청하기
: 사용자가 로그인에 성공하여 메인페이지로 이동하면 클라이언트는 EventSource객체를 생성하고 서버에 요청을 보내고, 서버에서 Emitter 객체 생성후 더미데이터를 보내주며 연결을 유지한다.

클라이언트의 코드는 똑같고, 컨트롤러에서 직접 생성해주던 Emitter 객체를 Service 클래스를 생성해줬다.
해당 컨트롤러에서 /connect 경로로 사용자마다 고유한 값인 empno를 붙여 요청을 보내오면, 서버에서는
text/event-stream 형식으로 응답한다. event-stream형식이란 서버와 클라이언트간 단방향 통신으로 일정한 양식으로 서버가 클라이언트에게 데이터를 전송한다.
서버에서 Emitter 객체 보관하기

<EmitterRepository 구현체>
@Repository
@NoArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class EmitterrepositoryImpl implements EmitterRepository{
private final Map<String, SseEmitter> emitters = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<String, Object> eventCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public SseEmitter save(String emitterId, SseEmitter sseEmitter) {
emitters.putIfAbsent(emitterId, sseEmitter);
log.info(""+emitters);
return sseEmitter;
}
@Override
public void saveEventCache(String eventCacheId, Object event) {
eventCache.put(eventCacheId, event);
}
@Override
public Map<String, SseEmitter> findAllEmitterStartWithById(String id) {
return emitters.entrySet().stream().filter(entry -> entry.getKey().startsWith(id))
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey,Map.Entry::getValue));
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> findAllEventCacheStartWithById(String id) {
return emitters.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> entry.getKey().startsWith(id))
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue));
}
@Override
public void deleteById(String id) {
emitters.remove(id);
}
@Override
public void deleteAllEmitterStartWithId(String id) {
emitters.forEach((key, emitter) -> {
if (key.startsWith(id)){
emitters.remove(key);
}
});
}
@Override
public void deleteAllEventCacheStartWithId(String id) {
emitters.forEach((key, emitter) -> {
if (key.startsWith(id)){
emitters.remove(key);
}
});
}
}
서버에서 특정한 이벤트가 발생하면, 클라이언트로 Emitter객체의 send 메소드를 통해 데이터를 전송한다.
즉, 사용자마다 고유의 id를 가진 Emitter가 있을것이고, 이벤트가 발생하면 해당 사용자의 Emitter의 cache값인 event를 전송하기때문에, 서버는 Emitter를 보관해야한다.
여러 자료들을 찾아보니 Emitter을 DB에 저장하기도 한다는데, 나의 경우 DB에 저장하지않고 서버의 Repository에서
ConcurrentHashMap 객체에 담아서 보관하며, 연결 종료시 삭제하는 방식을 사용하기로했다.
ConcurrentHashMap를 사용하는 이유는 다중스레드 환경에서 동시성 문제를 해결하기 위해 사용한다고 하는데,
아직 이부분은 정확히 이해하지못했다.
NotifycationService
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class NotificationService {
private static final Long DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = 60l * 1000 * 60;
private final EmitterrepositoryImpl emitterRepository;
public SseEmitter subscribe(String empno,String lastEventId) {
String id = empno + "_"+ System.currentTimeMillis();
SseEmitter emitter = emitterRepository.save(id, new SseEmitter(DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));
// 오류시 emitter 제거
emitter.onCompletion(()-> emitterRepository.deleteById(id));
emitter.onTimeout(() -> emitterRepository.deleteById(id));
// 더미데이터 전송
sendToclient(emitter,id,"EventStream 생성: [userID="+id+"]");
if(!lastEventId.isEmpty()) {
Map<String,Object> events = emitterRepository.findAllEventCacheStartWithById(String.valueOf(id));
events.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> lastEventId.compareTo(entry.getKey())<0)
.forEach(entry -> sendToclient(emitter,entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return emitter;
}
// 클라이언트에게 이벤트 발생시 emitter 보냄
public void sendEvent(String receiver,String notificationType,String msgTitle) {
Notification notification = createNotification(receiver,notificationType,msgTitle);
Map<String,SseEmitter> sseEmitters = emitterRepository.findAllEmitterStartWithById(receiver);
sseEmitters.forEach(
(key,emitter)->{
emitterRepository.saveEventCache(key, notification);
//데이터 전송
sendToclient(emitter, key, NotificationResponse.from(notification));
}
);
}
// Notification 객체 생성 메소드
private Notification createNotification(String receiver,String notificationType,String msgTitle) {
return Notification.builder()
.receiver(receiver)
.notificationType(notificationType)
.msgTitle(msgTitle)
.url("/connect/"+receiver) // 해당 url로 event 전송
.isRead(false)
.build();
}
private void sendToclient(SseEmitter emitter,String id,Object data) {
try {
emitter.send(SseEmitter.event()
.id(id)
.name("sse")
.data(data));
} catch (IOException e) {
emitterRepository.deleteById(id);
throw new RuntimeException("연결오류");
}
}
}
가장 중요한 NotifycationService이다.
1. subcribe() 메소드
: 맨처음 subcribe() 메소드를 통해 클라이언트가 서버에 구독을 요청할때, 사용자를 구분하기위해 id값을 같이보낸다.
서버에서 해당 id와 현재시간 Millitime을 사용하여 사용자마다 다른 Emitter 객체를 생성한뒤 repository.save로 저장한다.
2. SendEvent() 메소드
: 이벤트 발생시, 클라이언트에게 데이터를 보내기위해 사전 처리를 거친뒤,
내부메소드인 SendToClient()를 호출한다. 즉 실제로 클라이언트에게 메시지를 보내는건 SendToClient()이다.
그러므로 SendEvent()메소드를 각자의 비즈니스 요구사항에 맞게 알림을 전송하고싶은 이벤트 전송 시점에 호출하면 되는것이다.
나의 경우 메시지 작성시, DB에 메시지 정보를 저장한뒤, SendEvent() 메소드를 호출하여 메시지 관련 정보를 파라미터로 넣어주었다.
Notification 객체

Notification 객체는 알림에 관한 데이터들을 담기위해 만든 일종의 DTO이다.
알림에 담고싶은 내용들을 넣어주면 된다.
NotificationResponse

NotificationResponse 클래스는 Notification 객체가 클라이언트에게 전송될때, 클라이언트에게 맞는 형식으로 변환시켜주는 클래스이다.
서버에서 클라이언트로 Notification 객체가 Stream 방식으로 전송되므로 데이터 직렬화가 필요하다.
따라서 Notification에 객체를 담아주고싶은경우 해당 클래스에서 직렬화를 거쳐주면 된다.
나의 경우 처음에 Dto를 담았다가, 직렬화를 해주지않아 에러가 났었는데 굳이 객체의 모든정보가 필요하지않아
String형태의 title값만 빼서 넣어주었다.
2. 서버에서 특정 이벤트 발생시 클라이언트로 Emitter 전송
이제 서버에서 클라이언트로 알림을 보낼 준비가 다 되었으므로, 이벤트 발생 시점에 관련 데이터를 전송해주기만 하면 된다.
해당 메소드는 메신저기능에서 메시지를 작성하면 해당 메시지 Dto가 DB에 저장되는 메소드이다.
원하는 알림 이벤트 : 메시지가 작성 될때, 받는사람에게 알림전송이므로,
위에서 구현한 notificationService 클래스의 sendEvent 메소드를 통해 받는사람 id, 알림Type, 알림 제목을 넣어줬다. 해당 파라미터는 Notification객체에서 각자 필요한데로 수정하면 된다.
<메시지 작성 전>

콘솔에 EventStream 생성 로그만 출력되어있다.
즉, 연결에 성공하고 서버에서 데이터를 받기위해 기다리고있는 상태다.
<메시지 도착시>
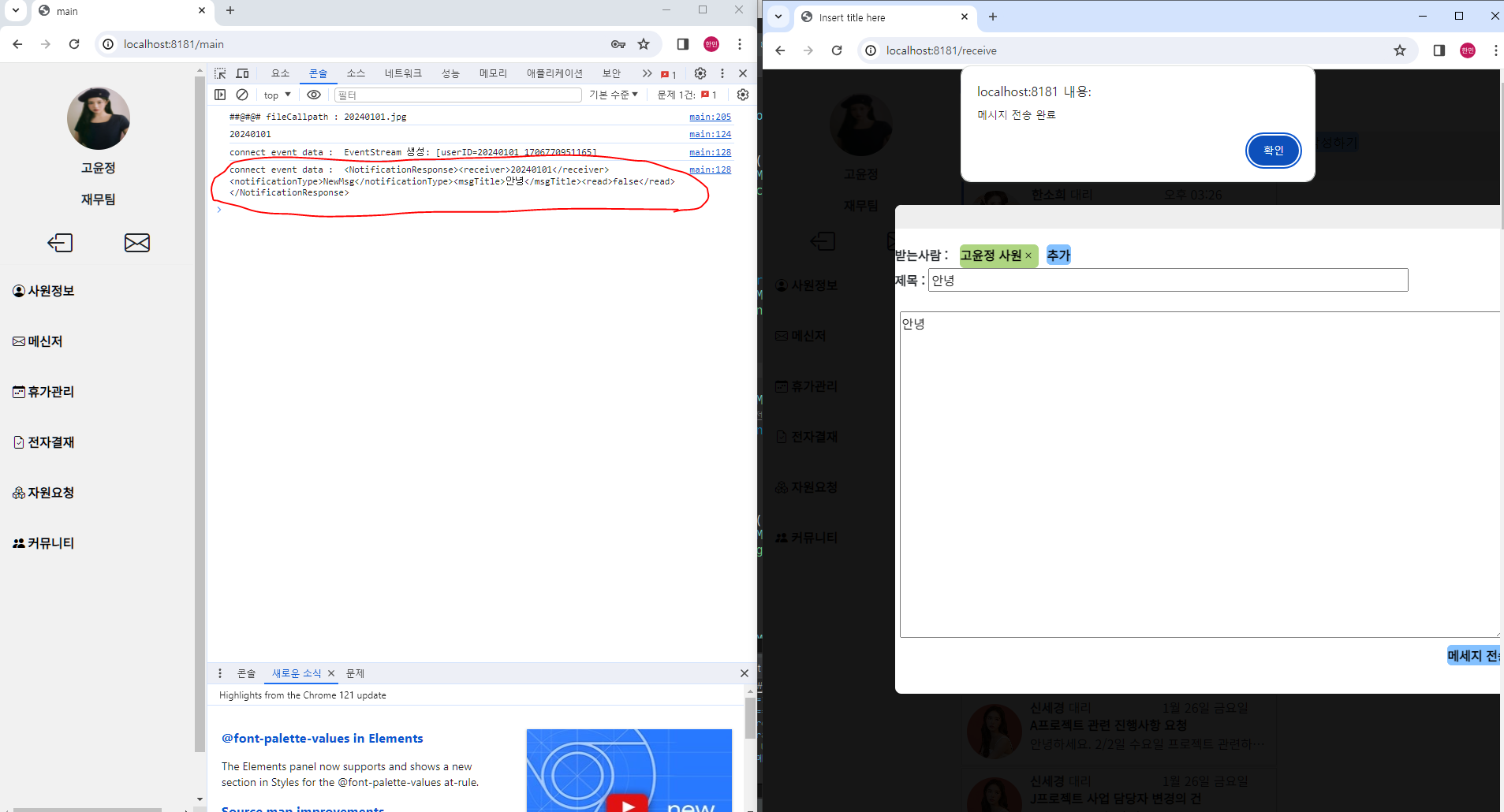
오른쪽 브라우저에서 왼쪽 브라우저로 메시지를 작성하면,
콘솔에 새로운 메시지의 정보가 담긴 데이터가 출력된다!!
정상적으로 통신에 성공했다.
이제 해당 데이터값을 가지고 제이쿼리를 이용하여 View에 알림표시 기능만 구현하면 완성이다!!
처음 Sse에 대해 공부했을때 뭐가뭔지 하나도몰라서 막막했지만 그래도 차근차근 하나씩 공부해나가며 원하는 기능을 구현해서 정말 다행이다.
해당 글은 다음의 게시글을 참고하여 개인적으로 공부한 내용으로, 정확하지않은 내용이 있을수있습니다.
<참고한 게시글 >
[Spring + SSE] Server-Sent Events를 이용한 실시간 알림
코드리뷰 매칭 플랫폼 개발 중 알림 기능이 필요했다. 리뷰어 입장에서는 새로운 리뷰 요청이 생겼을 때 모든 리뷰가 끝나고 리뷰이의 피드백이 도착했을 때 리뷰이 입장에서는 리뷰 요청이 거
velog.io
'Category > Project' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [개인프로젝트] 2일차 - 시큐리티 권한 세팅하기, 영속성 컨텍스트 (0) | 2024.02.19 |
|---|---|
| [팀프로젝트] 15일차 - Sse를 이용해 실시간 알림기능 구현2 (0) | 2024.02.02 |
| [팀프로젝트] 12일차 - 전자결재 시스템 만들기 (0) | 2024.01.30 |
| [팀프로젝트] Mybatis 매핑에러 - BindingException (0) | 2024.01.29 |
| [팀프로젝트] 10일차 - 메시지 기능 구현 (2) | 2024.01.28 |



